The six most important things you should know about fascia.
- Fascia function as intermediaries between the muscles and the bones. They provide more stability than muscles and at the same time provide more mobility than bones.
- Fascial tissues can be found in every part of our body. Every single cell is covered in fascia. If it were possible to remove the fascia covering, there would still remain an exact shell of the human body.
- Dr. Robert Schleip (Ulm University) has proved that fascia contain contractile elements. Continual stress leads to an increase in the fascial tonus through the autonomous nerve system that manifests itself as tension and stiffness.
- Fascia can be seen as being one of the sensory organs. They contain more nerve fibres than our skin or eyes for example. That is why a dysfunction of the fascia can lead to very strong pain.
- By means of fascial chains, tension is distributed throughout the whole body. Physiologically this helps to distribute exerted forces and weaken them. Pathologically this comes from a restriction in one area leading to an incorrect tension in an area that be far away from the original problem.
- Fascia support the muscles by means of contraction. They keep the muscles in shape and increase muscle strength. By pre-stretching, the fascia store energy, that is then released when they move together with the muscles (e.g. throwing a javelin).
Six typical fascial dysfunctions
Stephen Typaldos D.O. discovered six different dysfunctions within the fascia of the musculoskeletal system:
- Triggerband
- Continuum Distorsion
- Herniated triggerpoints
- Cylinder distortion
- Folding distortions
- Tectonic fixations
What is a triggerband?
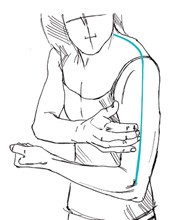 A trauma generally leads to a twisting or splitting of the fascial layer that leads to pain and restriction of movement. Fascia are always aligned so that they can divert any occurring forces.
A trauma generally leads to a twisting or splitting of the fascial layer that leads to pain and restriction of movement. Fascia are always aligned so that they can divert any occurring forces.
However, if a force is applied that is not in this but rather in a transverse direction to the alignment then this can lead to the fascia splitting. In the fascial distortion model, this condition of the fascia is called a triggerband.
The patients report a searing, burning pain that they indicate with several fingers moving along a line. In the clinic we find restriction of mobility due to a shortening of the triggerband, a loss of strength as well as reduction in stability and coordination.
The subsequent therapy is the derotation of the present rotation or the joining together of the split fascia. This is achieved with the aid of the therapist’s thumbs and with the application of great pressure and precision along the line indicated by the patient the problem is resolved. After it is sealed, the fascia are as good as before the trauma.
Due to FDM the description “chronic pain patient” takes on a completely new meaning. Up until now such patients were seen as being “incurable”. FDM sees persistent chronic pain in a completely new way. With chronic pain it can lead to an adhesion of the split in the triggerband by means of the crosslinks.
Due to excessive rest and restraint problems can occur not just with the crosslinks but also structures are combined that do not belong to each other. This leads to even more pain and also further mobility restriction.
Focused treatment by means of the triggerband technique causes the adhesion to dissolve; this in turn can lead to haematomas and an increase in pain. However this has the potential to heal as an acute triggerband is produced from a chronic dysfunction. By using the same technique during the second and third treatments the triggerband is sealed and the patient is now free of pain. After the treatment the patient is required to move so as to test whether the previous painful movement is now pain free.